What is a current state analysis?
A current state analysis is a process used to evaluate and understand the present-day situation of any given system. Looking at the Missouri Botanical Gardens, our system is the wicked problem of inequality in plant knowledge. There are 4 questions that we should ask ourselves as researchers for this process: 1) Where are we? 2) Where are we headed? 3) Where do we want to go? and 4) How do we get there?

A system can be best described as a set of interconnected components organized in such a way that they cannot act individually and achieve the same results. Regulation of these systems is conducted through direct drivers and indirect drivers. Direct drivers unequivocally impact the overall behavior of a system. Indirect drivers influence the system’s behavior in a more diffuse and subtle way. (Make sure to refer thinking in systems back to the textbook)
Our research problem in The Missouri Botanical Gardens is an example of a complex adaptive system meaning that it develops over time to adapt in a way that ensures its survival. When you approach this system using reductionist thinking, you can more clearly see how the components interact with each other on a smaller scale. Pictured below is a system of a few direct and indirect drivers that contribute to the issue of plant inequality at MOBOT.
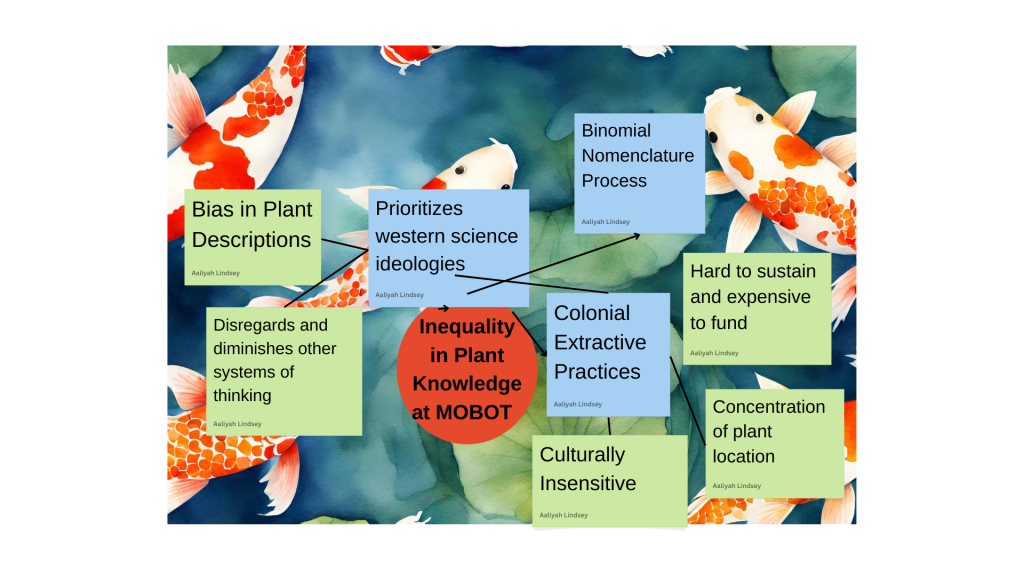
One of the most impactful direct drivers in this situation is the practice of colonialism extraction used to retreive the plants. This selection process is biased in every aspect incluidng where the plants are collected from, what plants are collected, and who collects the plants. Usually, white men get to decide all of these things which means that the plant selction is often rooted in personal biases and preferences. This breeds an indirect driver of cultural insensitivity. The people who depend on these plants locally often get no say in the extraction of these plants that have medicinal and nutritous uses for them. Taking these plants from their space and transporting it for research else where might provoke strong feelings of anger and despair.
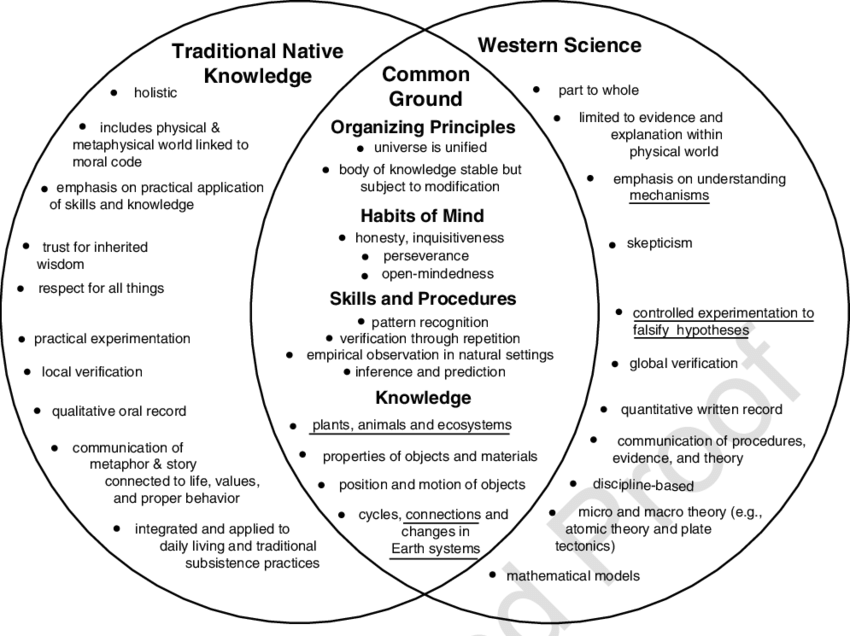
The prioritization of western science is another direct driver for our system. The complete disregarding or minimization of indigenous knowledge of plant has resulted in a collection of plant knowledge curated almost entirely by the minds of white men. Western science is based on things such as global verifacation, quantatative written record, and mathematical models. Traditonal Native knowledge is rooted in things such as qualitative world record, practical application, and holistic thinking. These two approaches to research and science should be carefully integrated and applied when collecting plant specimens and when the binomial nomenclature process is being conducted. Although these systems of thinking should be combined its essential that their is emphasis placed on the traditonal native knowledge because the plants are local to their areas and are heavily relied upon by the native people.

The names given to plants by the Native people are particularly important to understanding not only the cultural knoweldge surrounding it. It also gives entail about the uses of the plant.
Leave a Reply